Why low-cost ketamine is still inaccessible to many with severe depression
UNSW Sydney
A case study on ketamine reveals systemic barriers that prevent repurposing existing low-cost drugs like ketamine for treatment-resistant depression.
Patients with treatment-resistant depression are missing out on potentially life-changing treatment with ketamine because systemic barriers in the public health system have made it unaffordable.
In an article published recently in the Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, a multidisciplinary team of medical researchers, including UNSW Sydney, Black Dog Institute and The George Institute for Global Health, provided insights into why affordable, effective treatments are being eclipsed by novel more expensive alternatives that aren’t necessarily better. They discussed the challenges that are limiting access to affordable treatments and proposed solutions to overcome these barriers.
The researchers drew attention to the fact that it is now more than 20 years since the first indications that generic ketamine was effective, but public funding to support research and patient access has been slow, uncoordinated and underfunded. They also say there have been insufficient commercial incentives to conduct the research and development of generic ketamine, nor any schemes promoting public-private partnerships.
There is now a stark disparity in the accessibility and cost of ketamine-based depression treatments. The patented, intranasal s-enantiomeric ketamine formulation, Spravato, is priced at around $500 to $900 per dose, whereas generic ketamine stands at about $5 to 20 per dose. This high cost has led to Spravato being rejected for public reimbursement three times and thus it remains largely inaccessible for Australian patients.
On the other hand, generic ketamine, despite also being effective at a fraction of the cost, remains unapproved and underutilised due to regulatory and financial barriers. One such barrier is the cost of care of patients who must be monitored for at least two hours after receiving each dose – whether an injection with generic ketamine or nasal spray with Spravato – and as ongoing doses are needed for the treatment to be effective, the mounting costs can become prohibitive for many.
This narrative is not unique to ketamine, as the article foresees a similar fate for upcoming psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy treatments, which are on the verge of entering the mental health treatment arena. The article suggests that without systemic interventions, the cycle of underutilising low-cost effective solutions is set to continue, leaving patients unable to access treatments while threatening to blow out health care costs.
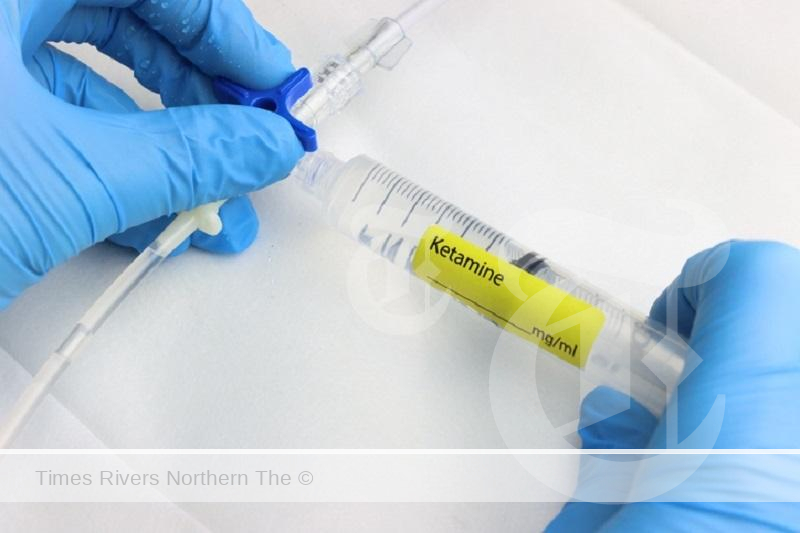
A case study on ketamine reveals systemic barriers that prevent repurposing existing low-cost drugs like ketamine for treatment-resistant depression.
Professor Anthony Rodgers from The George Institute, which is affiliated with UNSW Sydney, says he and his fellow colleagues propose a range of solutions including:
- providing better commercial incentives
- boosting funding for integrated and translational research
- reducing regulatory hurdles
- optimising clinical trial procedures, and
- fostering broader collaboration across sectors and borders
He calls on stakeholders across the board to rally towards creating a conducive ecosystem for repurposing off-patent medicines.
“Our findings accentuate an urgent need for structural reforms. It’s imperative that we harness collective efforts to ensure the affordable becomes accessible, ushering in a new era of mental healthcare that is both effective and economically sustainable,” Prof. Rodgers says.
Co-author Professor Colleen Loo, who is a clinical psychiatrist with the UNSW-affiliated Black Dog Institute, says she has witnessed remarkable results over the last 12 years using low-cost ketamine to treat severe depression that has not responded to other treatments.
“To make this treatment accessible to patients, Medicare funding of the treatment process is required, but the process is blocked by systemic barriers as explained in this paper,” Prof. Loo says.
“As there is no commercial gain for pharmaceutical companies in supporting a listing of low-cost, off-patent ketamine as a treatment for depression, the drug is not listed by the TGA for such use, and thus cannot attract Medicare funding for the treatment.
“This is despite all parties recognising that repurposing of existing, low-cost, off-patent drugs for new uses, is in society’s interest. We need government to intervene, to shift these barriers.”
The authors and their respective institutions are planning an application to Medicare to have ketamine treatment for severe depression supported by the government health system.
For more health news, click here.





 Tweed Shire News2 years ago
Tweed Shire News2 years ago
 Motoring News2 years ago
Motoring News2 years ago
 COVID-19 Northern Rivers News3 years ago
COVID-19 Northern Rivers News3 years ago
 COVID-19 Northern Rivers News3 years ago
COVID-19 Northern Rivers News3 years ago
 Northern Rivers Local News3 years ago
Northern Rivers Local News3 years ago
 Health News3 years ago
Health News3 years ago
 COVID-19 Northern Rivers News3 years ago
COVID-19 Northern Rivers News3 years ago
 NSW Breaking News3 years ago
NSW Breaking News3 years ago




























